Evolution of Microprocessors
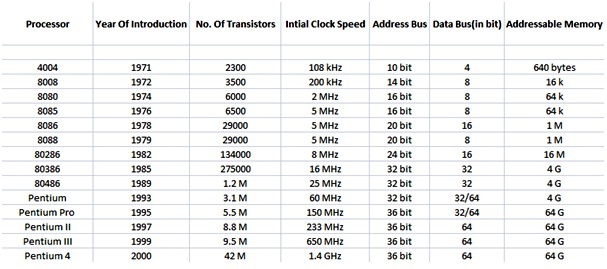
Table :- Intel Microprocessors Historical perspective
The first
Microprocessor (4004) was designed by Intel Corporation which was founded by Moore
and Noyce in 1968.
In the early
years, Intel focused on developing semiconductor memories (DRAMs and EPROMs)
for digital computers.
In 1969, a
Japanese Calculator manufacturer, Busicom approached Intel with a design for a small
calculator which need 12 custom chips. Ted Hoff, an Intel Engineer thought that
a general purpose logic device could replace the multiple components.
This idea led
to the development of the first so called microprocessor. So, Microprocessors started
with a modest beginning of drivers for calculators.
With
developments in integration technology Intel was able to integrate the
additional chips like 8224 clock generator and the 8228 system controller along
with 8080 microprocessor with in a single chip and released the 8 bit
microprocessor 8085 in the year 1976. The 8085 microprocessor consisted of 6500
MOS transistors and could work at clock frequencies of 3-5 MHz. It works on a
single +5 volts supply. The other improved 8 bit microprocessors include Motorola
MC 6809, Zilog Z-80 and RCA COSMAC.
In 1978, Intel
introduced the 16 bit microprocessor 8086 and 8088 in 1979. IBM selected the
Intel 8088 for their personal computer (IBM-PC).8086 microprocessor made up of
29,000 MOS transistors and could work at a clock speed of 5-10 MHz. It has a
16-bit ALU with 16-bit data bus and 20-bit address bus. It can address up to
1MB of address space. The pipelining concept was used for the first time to
improve the speed of the processor. It had a pre-fetch queue of 6 instructions
where in the instructions to be executed were fetched during the execution of
an instruction. It means 8086 architecture supports parallel processing. The 8088
microprocessor is similar to 8086 processor in architecture ,but the basic
difference is it has only 8-bit data bus even though the ALU is of 16-bit.It
has a pre-fetch queue of 4-instructions only.
In 1982 Intel
released another 16-bit processor called 80186 designed by a team under the leadership
of Dave Stamm. This is having higher reliability and faster operational speed
but at a lower cost. It had a pre-fetch queue of 6-instructions and it is suitable for high volume applications
such as computer workstations, word-processor and personal computers. It is made
up of 134,000 MOS transistors and could work at clock rates of 4 and 6 MHz.
This is also comes under first generation of Microprocessors.
Intel released another 16
bit microprocessor 80286 having 1, 34,000 transistors in 1981. It was used as
CPU in PC-ATs in 1982. It is the second generation microprocessor, more
advanced to 80186 processor. It could run at clock speeds of 6 to 12.5 MHz .It
has a 16-bit data bus and 24-bit address bus, so that it can address up to 16MB
of address space and 1GB of virtual memory. It had a pre-fetch queue of 6
instructions .Intel introduced the concept of protected mode and virtual mode
to ensure proper operation. It also had on-chip memory management unit (MMU)
.This was popularly called as Intel 286 in those days.
In 1985, Intel released
the first 32 bit processor 80386, with 275,000 transistors. It has 32-bit data
bus and 32-bit address bus so that it can address up to a total of 4GB memory
also a virtual memory space of 64TB.It could process five million instructions
per second and could work with all popular operating systems including Windows.
It has a pre-fetch queue of length 16-bytes with extensive memory management
capabilities. It is incorporated with a concept called paging in addition to
segmentation technique. It uses a math co-processor called 80387.
Intel introduced 80486
microprocessor with a built-in maths co-processor and with 1.2 million
transistors. It could run at the clock speed of 50 MHz This is also a 32 bit
processor but it is twice as fast as 80386.The additional features in 486
processor are the built-in Cache and built-in math co-processors. The address
bus here is bidirectional because of presence of cache memory.
On 19th October, 1992,
Intel released the Pentium-I Processor with 3.1 million transistors. So, the
Pentium began as fifth generation of the Intel x86 architecture. This Pentium
was a backward compatible while offering new features. The revolutionary
technology followed is that the CPU is able to execute two instruction at the
same time. This is known as super scalar technology. The Pentium uses a 32-bit
expansion bus, however the data bus is 64 bits.
The 7.5 million
transistors based chip, Intel Pentium II processor was released in 1997. It works
at a clock speed of 300M.Hz. Pentium II uses the Dynamic Execution Technology
which consists of three different facilities namely, Multiple branch
prediction, Data flow analysis, and Speculative execution unit. Another
important feature is a thermal sensor located on the mother board can monitor
the die temperature of the processor. For thermal management applications.
Intel Celeron Processors
were introduced in the year 1999. Pentium-III processor with 9.5 million
transistors was introduced in 1999. It also uses dynamic execution
micro-architecture, a unique combination of multiple branch prediction,
dataflow analysis and speculative execution.
The Pentium III has
improved MMX and processor serial number feature. The improved MMX enables advanced
imaging, 3D streaming audio and video, and speech recognition for enhanced
Internet facility.
Pentium-IV with 42 million
transistors and 1.5 GHz clock speed was released by Intel in November 2000. The
Pentium 4 processor has a system bus with 3.2 G-bytes per second of bandwidth.
This high bandwidth is a key reason for applications that stream data from
memory.
This bandwidth is achieved
with 64 –bit wide bus capable of transferring data at a rate of 400 MHz. The
Pentium 4 processor enables real-time MPEG2 video encoding and near real-time MPEG4
encoding, allowing efficient video editing and video conferencing.
Intel with partner
Hewlett-Packard developed the next generation 64-bit processor architecture called
IA-64 .This first implementation was named Itanium. Itanium processor which is
the first in a family of 64 bit products was introduced in the year 2001.The
Itanium processor was specially designed to provide a very high level of
parallel processing ,to enable high performance without requiring very high
clock frequencies .Key strengths of the Itanium architecture include ,up to 6
instructions/cycle. The Itanium processor can handle up to 6 simultaneous 64
–bit instructions per clock cycle.
The Itanium II is an IA-64
microprocessor developed jointly by Hewlett-Packard (HP) and Intel and released
on July 8,2002..It is theoretically capable of performing nearly 8 times more
work per clock cycle than other CISC and RISC architectures due to its parallel
computing micro-architecture. The recent Itanium processor features a split L2
cache, adding a dedicated 1MB L2 cache for instructions and thereby effectively
growing the original 256KBL2 cache, which becomes a dedicated data cache. The
first Itanium 2 processor (code named McKinley) was more powerful than the
original Itanium processor, with approximately two times performance.
Pentium 4EE was released
by Intel in the year 2003 and Pentium 4E was released in the year 2004.
The Pentium Dual-Core
brand was used for mainstream X86-architecture microprocessors from Intel from
2006 to 2009 The 64 bit Intel Core2 was released on July 27,2006. In terms of
features, price and performance at a given clock frequency, Pentium Dual-Core
processors were positioned above Celeron but below Core and Core 2 microprocessors
in Intel's product range. The Pentium Dual-Core was also a very popular choice
for over clocking, as it can deliver optimal performance (when over clocked) at
a low price.
The Pentium Dual Core,
which consists of 167 million transistors was released on January 21, 2007.
Intel Core Duo consists of two cores on one die, a 2 MB L2 cache shared by both
cores, and an arbiter bus that controls both L2 cache and FSB access.
Core 2 Quad processors are
multi-chip modules consisting of two dies similar to those used in Core 2 Duo,
forming a quad-core processor. While this allows twice the performance to a
dualcore processors at the same clock frequency in ideal conditions, this is
highly workload specific and requires applications to take advantage of the
extra cores.
In September.2009, new
Core i7 models based on the Lynnfield desktop quad-core processor and the Clarksfield
quad-core mobile were added, and models based on the Arrandale dualcore mobile
processor have been announced. The first six-core processor in the Core lineup
is the Gulftown, which was launched on March 16, 2010. Both the regular Core i7
and the Extreme Edition are advertised as five stars in the Intel Processor
Rating.
REFERENCES
- R. S. Gaonkar, Microprocessor Architecture, Programming, and Applications with the 8085, Fifth Edition, Penram International Publishing (India) Private Limited.
- S Ghoshal, Microprocessor Based System Design, Macmillan India Limited, 1996.
- M. Mano, Digital Logic and Computer Design, Prentice – Hall India.
- B. Ram - Fundamentals of Microprocessor and Microcontrollers.
- “Microprocessors: Principles and Applications” by A Pal.
- “Microprocessors and Microcontrollers : Architecture, Programming and Interfacing Using 8085, 8086 and 8051” by Soumitra Kumar Mandal.
- “Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers” by Crisp John Crisp.
- “Microprocessors And Microcontrollers” by A Nagoor Kani.
- “Microprocessors And Microcontrollers : Architecture, Programming and System Design 8085, 8086, 8051, 8096” by Krishna Kant.
- “8 - Bit Microprocessor” by Vibhute
Comments
Post a Comment